Emergency medical services are a critical one and a career within it can be lucrative. It’s all about saving and providing life-saving care. It’s a field that provides tremendous growth opportunities and a high demand for qualified professionals. In this post, we’ll guide you through the process to become an EMT or paramedic, examining the various training options available that include a DSHS certified EMS training course.
Understanding the Role and Function of EMTs, Paramedics
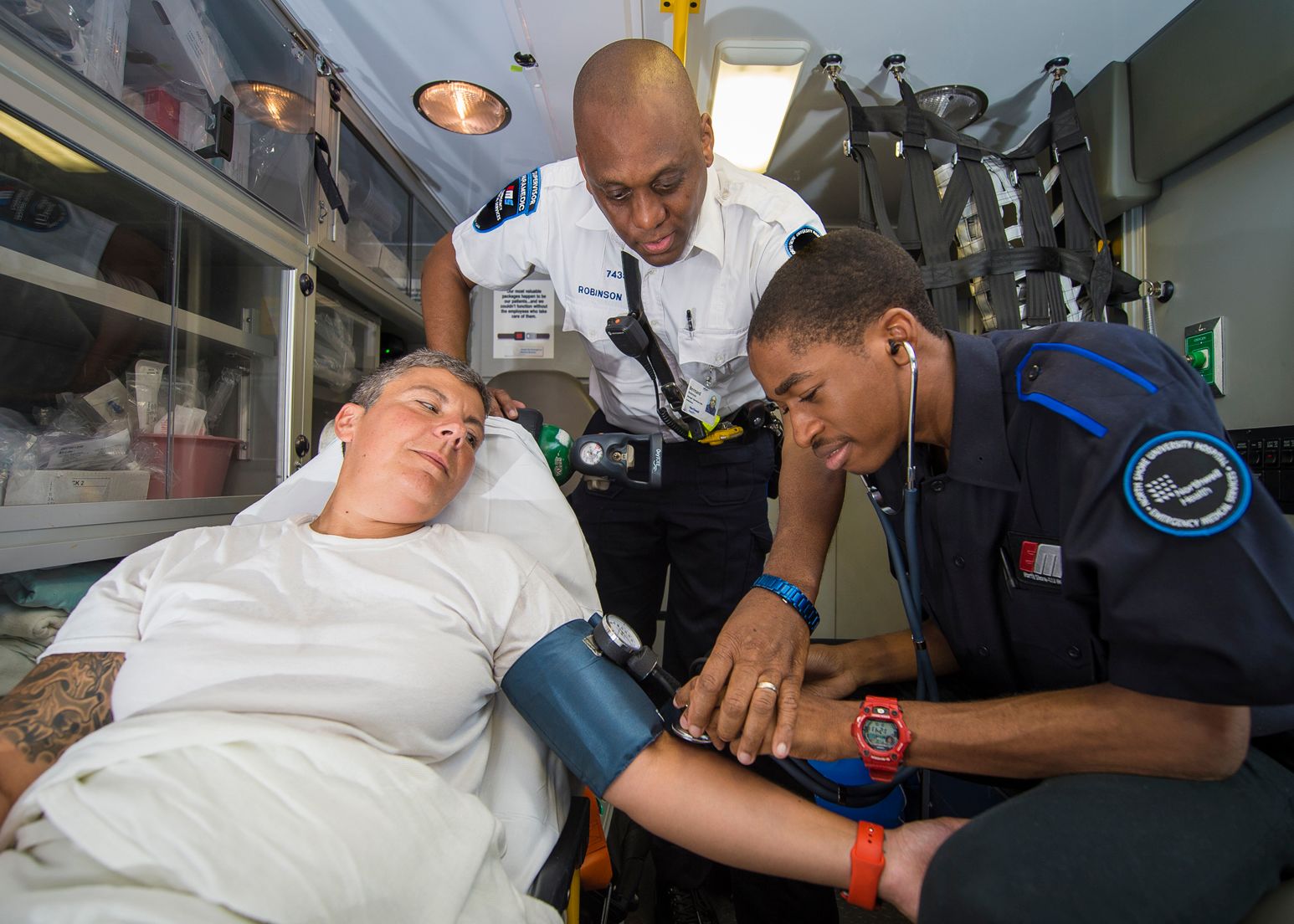
Emergency Medical Technicians commonly referred to paramedics or EMTs are the first emergency responders. They provide immediate medical care. They are trained to evaluate patients, administer essential medical procedures, and transfer patients in a safe way to medical facilities for treatment. Paramedics and EMTs are vital in stabilizing patients in critical situations, deciding in split-seconds, and providing compassionate assistance during times of stress.
Step 1: Becoming EMT
To be an EMT you’ll need to complete a variety of education and training courses. These may differ based on the degree of certification you want to attain. There are three levels to EMT certification are available:
1. EMT-Basic (EMT-B) EMT-Basic (EMT-B): This is the simplest certification and needs between 100 and 150 hours of education. EMTs-B are certified in the basics of medical treatment, including CPR blood pressure control, and the basics of managing airways.
2. EMT-Intermediate (EMT-I) EMT-I demands an additional level of training and may vary between states. In some states, this degree is complemented by EMT-B. In other places the range of training is from 200 to 400 hours, and may include advanced medical skills as well as intravenous therapy and other skills that are enriched.
3. EMT Paramedic (EMT P) EMT-P is the highest level of certification for EMTs. The education required to earn this credential typically runs from 1000 to 1,800 hours. Paramedics have advanced skills in medical procedures such as administering medications, reading EKGs and managing airways.
Step 2: Obtaining paramedic certification
You must finish the EMT B or EMT I level before becoming a paramedic. You can then enroll in the paramedic training program, which lasts between one and two years. In this intensive instruction, you’ll learn about advanced medical topics and gain the skills and knowledge needed to manage critical situations in a professional manner.
Step 3: Exploring EMT Training Options:
You’re able to choose among a number of options for EMT certification, based upon the level you’d like to attain. EMT classes are typically offered through medical trade schools as well as community colleges at all certification levels. The programs are a combination of teaching in the classroom with hands-on experience and clinical as well as field environments.
Universities and colleges offer EMT programs at the level of EMT/Paramedic If you’re looking for an extensive, in-depth EMT program that can lead to the degree of a college. These programs provide you with more understanding of emergency services as well as a wider perspective on medical decision-making.
Step 4: Ensure that DSHS-approved EMS training
For aspiring EMTs and paramedics, it’s essential to make sure that the training course you select is DSHS approved. The Department of State Health Services accepts EMS courses to make sure that they adhere to the highest standards for competency and training. By enrolling in a DSHS approved EMS training course, you can rest assured that you are receiving top-notch instruction and meeting the necessary requirements for certification.
An occupation as an EMT or paramedic can be extremely rewarding and well-respected. EMTs and Paramedics are first emergency responders and play a crucial role in saving and offering immediate medical care during emergency situations. In order for those who want to become EMTs or paramedics to begin this life-saving journey they must finish all the necessary training and education programs. People can choose from a number of EMT programs, based upon their desired certification level. These include medical schools, community colleges and university programs.
It is essential to think about the training options available and make sure the EMS training course you choose to take is approved by the DSHS. You can be confident that the training you receive will meet the standards required to obtain EMT or paramedic accreditation.
As the need for qualified emergency medical specialists increases, EMS provides a wealth of career opportunities as well an opportunity to make a difference in the lives of those around you. You can start your career as an EMT or work your way towards becoming a paramedic. Your commitment to providing vital medical care will pay off with an enjoyable job.
